- HOME
- For Patients
- Artery dissection
- Symptom of artery dissection
Artery dissection
- About of artery dissection
- Cause of artery dissection
- Symptom of artery dissection
- Diagnosis of artery dissection
- Treatment of artery dissection
Symptom of artery dissection
Headache, cerebral infarction, and subarachnoid hemorrhage may occur.
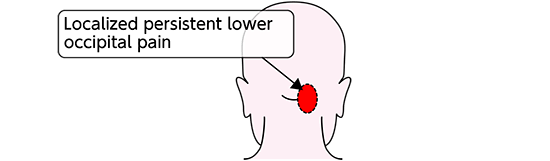
Headache
This pain is caused by the rupture of the vascular wall. Vertebral artery dissection, the most common form, causes a distinctive headache. This consists of persistent pain on one side of the occipital region that is so localized that the patient can point to the source of the pain with a finger.
Cerebral infarction
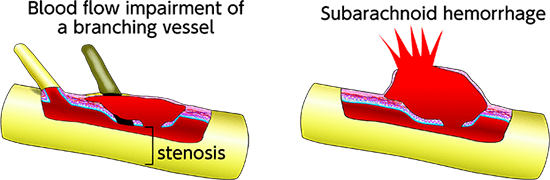
Blood flow to the fine branching vessels that split off from the ruptured blood vessel may be impaired, or blood flow may be reduced because narrowing (stenosis) of the ruptured blood vessel itself prevents it from passing through. Depending on the site of impaired blood flow, the limbs may be paralyzed, and sensory disturbance, dizziness, nausea, and other symptoms may appear.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
When blood flows into the vascular wall, it can cause its outermost layer, the tunica externa, to rupture.
The symptoms depend on the severity of the bleeding. In mild cases, it causes headache, nausea, and vomiting; if it becomes severe, it causes loss of consciousness, and in the worst case, it may be fatal. It tends to be more severe than subarachnoid hemorrhage due to usual cerebral aneurysm rupture.