- HOME
- For Patients
- Carotid stenosis
- Treatment of carotid stenosis
Carotid stenosis
- About carotid stenosis
- Symptom of carotid stenosis
- Diagnosis of carotid stenosis
- Treatment of carotid stenosis
Treatment of carotid stenosis
Surgery is performed if the stenosis is severe
In addition to quitting smoking and undertaking exercise and dietary therapy, the basic treatment is medical therapy with drugs for conditions such as hypercholesteremia, hypertension, and diabetes. Antiplatelet agents that improve blood flow and make it more difficult for blood to clot may also be added to prevent stroke. In most patients, stroke can be averted by improving lifestyle factors and starting drug therapy. However, if the narrowing of the carotid artery is severe, surgery may be more effective than drug therapy alone for improving the stenotic region and preventing stroke. There are two types of surgery, one involving opening the carotid artery and directly removing the atherosclerosis (this is known as "carotid endarterectomy") and another using a catheter to expand the stenosis from inside the vessel (this is known as "carotid artery stenting"). Which of these methods is chosen depends on the condition of the arteriosclerosis and the vessel, as well as the systemic condition and personal preferences of the patient. The criteria for performing surgery to prevent stroke are as follows. If only carotid artery stenosis has been found, with no cerebral symptoms, surgery to improve the carotid artery lesion should be performed if the diameter of the stenotic region is less than 20% that of the unaffected vessel. However, if cerebral infarction or other cerebral symptoms are present, surgery should be performed to prevent the exacerbation of stroke, even if lesions are only 50% narrower in diameter.
[ Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) ]
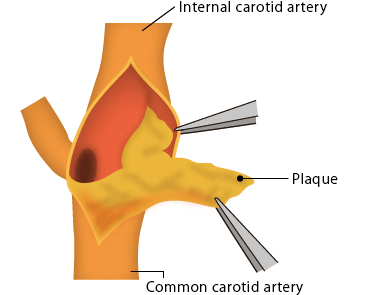
Carotid plaque is removed from the carotid artery under general anesthesia.
The carotid artery is temporary occluded and incised for the plaque removal.
Carotid artery stenosis is a disease of the blood vessels that carry blood to the brain, and the purpose of treatment is to prevent stroke. To ensure appropriate treatment, it is important to receive a diagnosis from specialists in stroke and neuroendovascular therapy who have a good knowledge of brain function. In the Department of Neurosurgery at Tokai University Hospital, several supervisors and specialists in stroke and neuroendovascular therapy investigate their own patients in order to be able to recommend the optimum treatment for each individual. People with carotid artery stenosis frequently have stenosis of other blood vessels as well. At Tokai University Hospital, if lesions of other vessels are also present, we provide comprehensive blood vessel treatment in collaboration with other departments such as the Department of Cardiology.
[ Carotid stenting ]
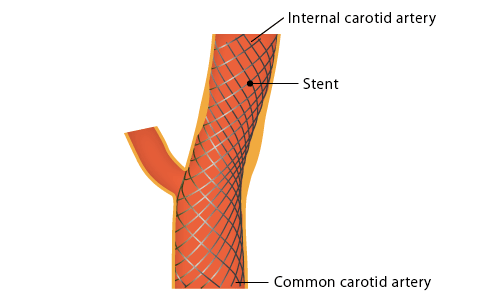
A balloon catheter is introduced into the carotid stenosis, then the balloon is inflated to widen the stenosis. A stent is placed in the carotid stenosis to maintain the widening of the stenosis. A patient is awake during the procedure with local anesthesia.
General procedure for surgery for carotid artery stenosis
- Carotid artery physical examination, ultrasound, MRA, CT angiography (CT while receiving an injection), blood tests, cardiac tests, ABI (a test to evaluate stenosis of blood vessels in the arms and legs) and cerebrovascular perfusion tests as an outpatient.
- Admission to hospital for cerebral angiography (catheterization).
- Consultation about surgery on an outpatient basis.
- Admission to hospital for surgery. If everything goes smoothly, the usual stay in hospital is one week or less for stenting and two weeks or less for endarterectomy.