- HOME
- For Patients
- Parkinson disease
- Details of surgical treatment
Parkinson disease
- About Parkinson disease
- Symptom of Parkinson disease
- Other symptoms of Parkinson's disease
- Cause of Parkinson disease
- Diagnosis of Parkinson disease
- Treatment of Parkinson disease
- Details of surgical treatment
- Surgical treatment of Parkinson disease
- Timing of surgery
- About our team
Details of surgical treatment
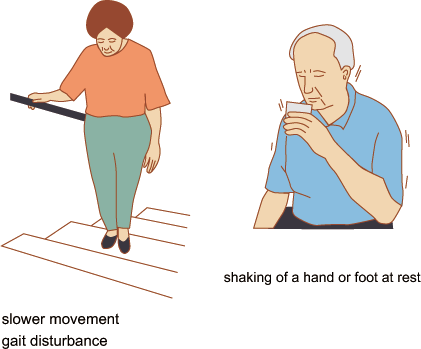
Movements such as tremors (shaking of the hands and feet) that occur involuntarily are closely related to brain activity.
Treatment for such involuntary movements basically consists of drug therapy, but medication taken over the long term becomes less effective, meaning that larger doses and/or wider ranges of medications become required. This can mean shorter intervals between doses and the appearance of severe side effects, leading to patients being unable to take their medication as intended and experiencing difficulties with activities of daily living. They become ever more conscious of attention from people, and tend to shut themselves away indoors.
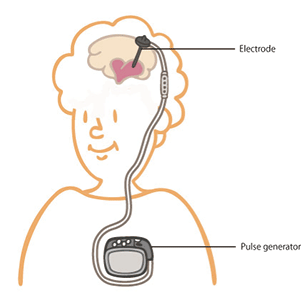
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a treatment that can offer a lifeline to such patients. It consists of the implantation of a tiny electrode into the part of the brain that controls the fine movements of the hands and feet, sending signals to the nerves and tuning the electrical impulses transmitted to the hands and feet from the brain. The best-known and longest-established procedure that involves sending electrical signals within the human body is treatment for arrhythmias, in which the electrical impulses of the heart become disturbed. In DBS, this cardiac-stimulating treatment is instead applied to the brain. DBS is now well established as an effective method of treatment, and is therefore covered by health insurance. By 2006, over 2,500 people had undergone DBS in Japan.
Schema of DBS
Result of DBS
Worldwide, DBS has been used to treat over 30,000 patients.
In 80% of patients, tremors stop completely during stimulation or become sufficiently mild so as not to impede activities of daily living, and these patients are able to decrease the doses and types of different medications they take, or to extend the interval between doses and take medication less frequently. By enabling the intensity of signals and other factors to be controlled after surgery, DBS can reduce the severity of tremors over a long period.
Effect of symptoms
In addition to tremors, DBS also has some effect on the freezing and gait disturbance seen in patients with Parkinson's disease.
DBS also improves the level of "off" times when the effectiveness of medication declines, and may reduce medication-induced dyskinesia (involuntary movements), meaning that DBS can be expected to smooth out daily variations in the effectiveness of medication.
Ask your attending physician
Patients who are dissatisfied with the effectiveness of drugs, for reasons such as being unable to take sufficient medication because of severe side effects due to increased doses or numbers of medication, experiencing dyskinesia due to medication, or having to take medication several times a day, should ask their attending physician to refer them to a neurosurgeon for a consultation.
Summary of DBS
- DBS utilizes a medical device with a long-standing record of use in applications such as cardiac pacemakers, has been implanted in over 30,000 patients worldwide and has also achieved good results in Japan.
- Following surgery, the pulse-generating device can be adjusted from outside the body, restoring neural tuning in accordance with the condition of the individual patient.
- Fine adjustments to the site of stimulation can also be made from outside the body while examining the condition of the patient after surgery.
- The electrode is tiny and is implanted in the brain by a specialist surgeon who has undergone in-depth training, making this a safe procedure.
- The site of electrical stimulation is confirmed by computer on a high-resolution map, and the electrode is placed very carefully while monitoring the communication between nerves during surgery.
- This treatment method offers a new option for patients who are worried about the side effects of medication or who are dissatisfied with its effectiveness.
- Treatment is covered by health insurance.
Deeply discuss with Neurosurgeon before surgery
- The effects of DBS are very similar to those of drugs such as L-dopa, and this treatment will not improve symptoms that are unaffected by medication or give better results than those provided by medication.
- DBS does not work on every symptom, and is not equally effective in all patients.
- DBS is a surgical procedure performed by a neurosurgeon.
- Although extremely rare, postoperative complications may occur, including infection due to bacteria entering the body, rejection reactions to the implanted device, damage to cerebral blood vessels (hemorrhage), and nerve dysfunction.
- Complications due to surgery are extremely rare. The neurosurgeon will provide a full explanation before the operation.
Combination between the medical and the surgery
Although DBS may enable a reduction in the dose and number of types of medication, this does not mean that patients can stop taking medication entirely. DBS exerts its effects in combination with drug treatment.
[ Fig : Effectiveness of DBS ]
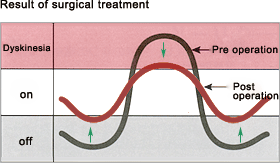
DBS reduces "off" times and dyskinesia, and can be expected to smooth out variations in the effectiveness of medication.
Side effect of DBS
Many people feel both hopeful and worried about undergoing DBS. The procedure for placing an electrode in a specific part of the brain has been carried out for many years. One issue people often worry about is side effects. In particular, surgery can result in serious complications, such as entry of bacteria into the brain or hemorrhage. The frequency of complications is often very different between Japan and other countries, so it is important to ask for this to be explained in detail before undergoing surgery.
Although extremely rare, DBS has been known to cause difficulties in impulse control when the intensity of stimulation is increased. In extreme cases, patients may become addicted to gambling, spend all their time shopping on the Internet, become unable to resist their sexual impulses, or put on excessive weight due to overeating. In such cases, a psychiatrist and neurosurgeon will work closely together to adjust brain stimulation and medication to appropriate levels in an effort to stabilize these symptoms.
Of course, the progress of the condition, effectiveness of surgery, and types and severity of side effects will vary from patient to patient. We have provided a simple summary here of what can be expected to happen for most patients, based on past results.
Neurologists and neurosurgeons take full account of previous treatments when considering what treatment method to use next for patients thinking about surgery.
In Japan, DBS is carried out on the basis of extensive experience, and patients can feel as safe undergoing this surgery as they do in taking medication.